DAO Governance Models: Navigating the Future of Decentralized Organizations
In 2024, decentralized finance (DeFi) witnessed over $4.1 billion losses due to hacks, highlighting the paramount importance of security and governance within blockchain ecosystems. As organizations strive for autonomy and inclusivity, DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) governance models emerge as a cornerstone in redefining community engagement, financial management, and operational efficiency. This article explores various DAO governance models, their implications in the blockchain landscape, and their relevance to the potential growth in the Vietnamese crypto market.
The Essence of DAO Governance
The core idea behind DAOs is to facilitate decentralized decision-making, disallowing any single entity from dominating the governance process. The governance models adopted by a DAO significantly impact its operational success, community involvement, and overall resilience against threats. According to a report by Deloitte, there has been a staggering growth of DAO frameworks, with a 300% increase in active DAOs in 2024 alone.
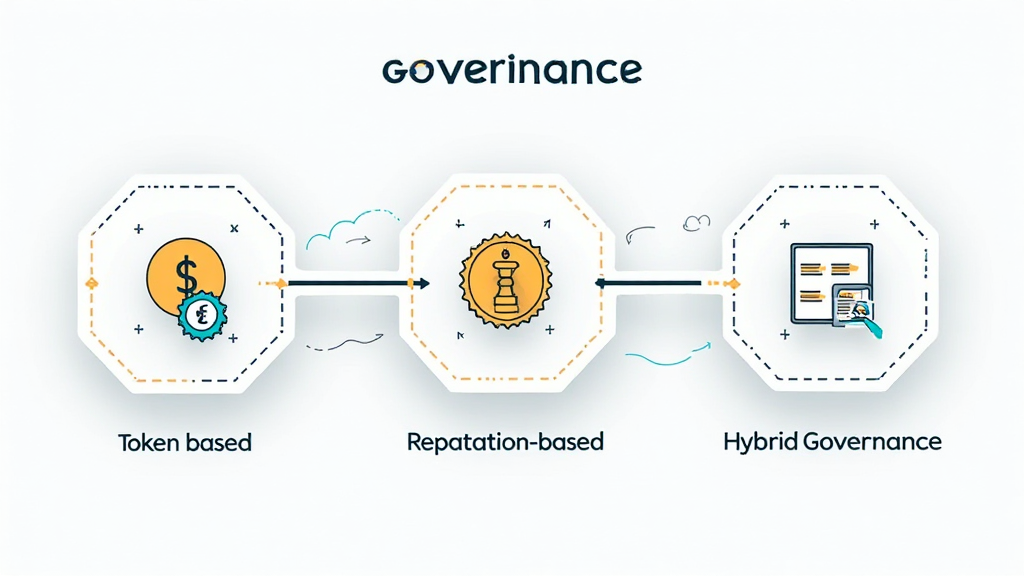
Types of DAO Governance Models
- Token-Based Governance: Decision-making rights are allocated based on the quantity of tokens held by members.
For instance, if a member holds 10% of the total tokens, they would have a proportional influence on governance decisions. - Reputation-Based Governance: Governance rights are tied to members’ reputation within the community rather than token holdings.
This model places emphasis on contributions and trust, drawing parallels with traditional social credit systems. - Hybrid Governance: Combining both token-based and reputation-based systems to create a more balanced approach.
This model offers flexibility and potential for greater community engagement while mitigating risks associated with singular governance methods.
Understanding Decision-Making Processes in DAOs
At the heart of DAOs lies how decisions are made, which can significantly impact their effectiveness. Decision-making processes can vary widely, influenced by the governance model adopted. The mechanics of proposals, voting, and execution must be clearly defined to avoid inefficiencies.

Proposal Submission and Voting Mechanics
In many DAOs, members can submit proposals concerning changes, funding allocations, or policy amendments. Once a proposal is submitted, it typically enters a voting phase that determines its acceptance or rejection.
- Quorum Requirements: Some DAOs establish a minimum number of votes (quorum) before a proposal can be executed, ensuring broad participation.
- Voting Duration: The time frame for which the vote is open can vary. Shorter voting periods may accelerate decision-making but can also lead to less consideration.
The Relevance of DAOs in Vietnam
With the Vietnamese crypto market experiencing rapid growth, understanding DAO governance models becomes crucial. As of 2024, Vietnam boasts a staggering user growth rate of 275% in cryptocurrency adoption, emphasizing the need for robust governance within emerging DAOs.
Community Engagement Strategies in Vietnam
To truly harness the potential of DAOs in Vietnam, engaging local communities through education and participation initiatives is essential. Many organizations have begun organizing workshops and webinars to demystify DAOs and their governance structures.
- Local Partnerships: Collaborating with local influencers and community leaders can foster trust and encourage participation within DAO governance.
- Incentivization: Offering tangible incentives such as token rewards for participation in governance processes can motivate community involvement.
Challenges in DAO Governance
DAO governance models, while revolutionary, are not without their challenges. Issues surrounding security, decentralization, and potential for malicious behavior must be carefully navigated.
Security Vulnerabilities
Like all digital systems, DAOs are subject to security vulnerabilities that could lead to significant financial losses. For example, smart contract bugs can be exploited, and token-based governance can be manipulated through acquisition of large amounts of tokens.
- Auditing Smart Contracts: Regular security audits by reputable firms are essential for identifying and mitigating risks.
- Community Vigilance: Encouraging community members to participate in monitoring and reporting suspicious activities fosters a more secure governance environment.
The Future of DAO Governance Models
As the landscape of cryptocurrency evolves, so too will the models governing DAOs. We can anticipate innovations that will address the limitations of existing frameworks, enhancing security and efficiency.
Emerging Trends in DAO Governance
In 2025 and beyond, we expect to see:
- Greater Decentralization: Continued movement towards removing centralized controls to strengthen DAO autonomy.
- Advanced Security Protocols: Integration of innovative security measures to protect against hacks and governance attacks.
- Inter-DAO Collaboration: DAOs forming strategic alliances to tackle big issues collectively, such as environmental sustainability or social equity.
Conclusion
DAO governance models are swiftly becoming the backbone of decentralized organizations, encapsulating the aspirations of financial freedom, security, and democratic governance. In light of the rapid growth of cryptocurrency adoption in Vietnam, understanding these models is essential for fostering effective community engagement and operational excellence. Look for future innovations in DAO governance that will continue to reshape the blockchain landscape, ensuring it remains both resilient and inclusive. Explore more about DACs and their impacts on local and global markets. For an in-depth look into blockchain standards, visit hibt.com.
Moreover, as with any financial endeavor, it is imperative to conduct thorough research and consult local regulators.
Author: Dr. Minh Nguyen, a blockchain technology expert with over 15 published papers in the field and has overseen audits for prominent blockchain projects.