Understanding BTCMajor: HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO Governance and Quorum Rules
In 2024, decentralized finance (DeFi) has already suffered over $4.1 billion in losses due to hacks and exploitations. This staggering amount raises significant questions about security standards and governance within blockchain ecosystems, especially for platforms like BTCMajor, which combines innovative technologies with local markets. Today, we delve into the essential aspects of HIBT Vietnam bond DAO governance and quorum rules.
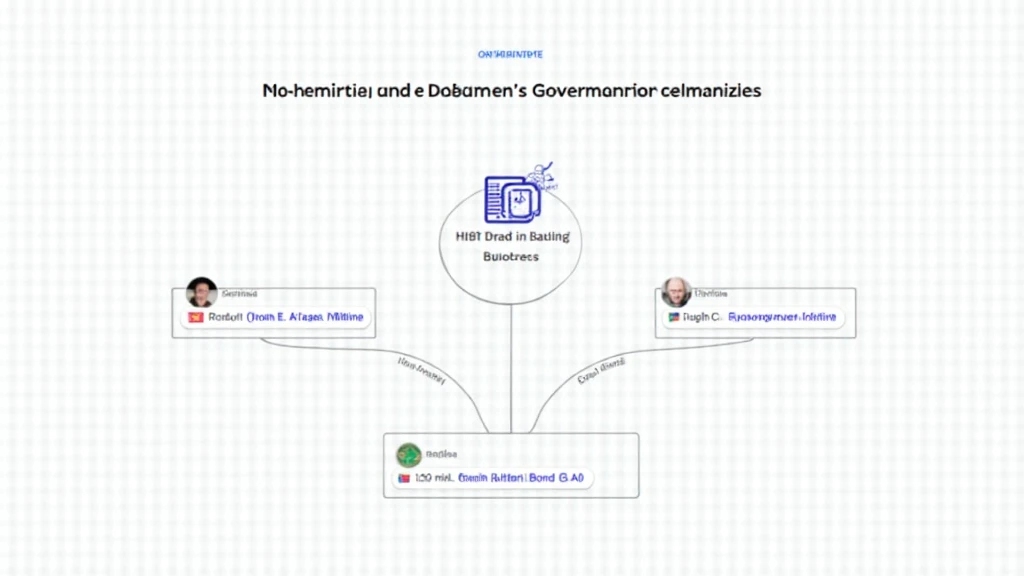
What is the HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO?
The HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO represents a fusion of traditional financial instruments and advanced blockchain technology, reflective of Vietnam’s unique financial landscape. Designed to govern and manage bond issuance through decentralized protocols, this DAO harnesses the strength of community decision-making.
According to recent studies by the Vietnam Blockchain Association, Vietnam’s blockchain user growth rate is 263% year-on-year. This exponential increase shows a rising interest in decentralized applications, particularly DeFi and DAOs, which strengthens the relevance of initiatives like the HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO.

The Importance of Governance
Governance within a decentralized ecosystem is akin to a community-run initiative where stakeholders actively participate in decision-making processes, thereby eliminating central authority. The primary benefits include:
- Transparency: Provides a clear structure for decision-making.
- Inclusion: Empowers a wide range of participants in governance through voting mechanisms.
- Efficiency: Facilitates faster decision-making processes without traditional bottlenecks.
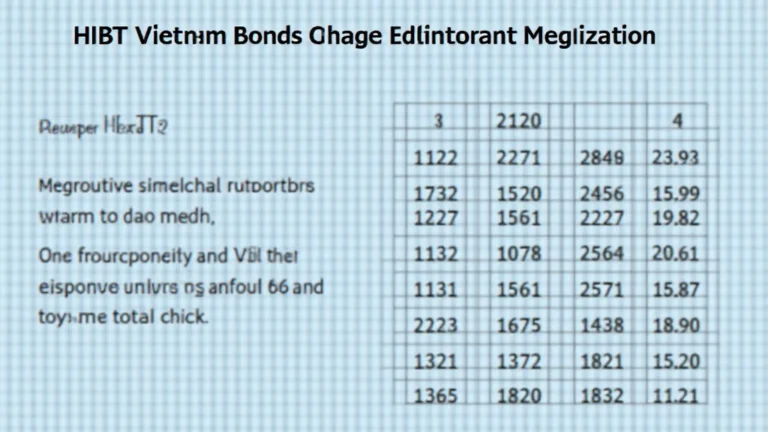
Quorum Rules in the HIBT DAO
Quorum rules refer to the minimum number of votes required for a proposal to be valid. These rules are essential in ensuring that a proposal has enough support to warrant consideration. Below are some of the quorum rules that govern the HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO:
- Minimum Vote Requirement: Typically requires at least 50% of stakeholders to participate in voting.
- Threshold for Approval: A proposal must receive at least 60% approval to pass.
- Time Limitations: Votes must be cast within a specified time frame, encouraging timely participation.
Common Challenges in DAO Governance
While DAOs offer innovative governance solutions, they also face challenges that can affect their operations.
- Voter Apathy: Low turnout can lead to skewed results.
- Complexity of Proposals: Technical jargon may discourage participation.
- Manipulation Risks: Vulnerabilities that can lead to influence by a small group.
Strategies to Mitigate Challenges
To combat challenges associated with DAO governance, the HIBT initiative can adopt several strategies:
- Add gamification to engage participants, similar to how video games incentivize action.
- Provide comprehensive educational tools to clarify governance structures.
- Establish a watchdog committee to oversee fair practices.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Governance
Advanced technologies can boost governance efficiency significantly. Here are a few ways technology enhances DAO governance:
- Smart Contracts: Automate processes such as voting and fund distribution, minimizing human error.
- Blockchain Transparency: Creates an immutable record of proposals, votes, and decisions made.
- Real-time Data Metrics: Allow participants to analyze and review ongoing governance-related metrics.
Real-World Examples of DAO Governance
To comprehend the practical implementation of DAO governance, let’s analyze a few real-world examples:
- The DAO: Although it faced significant challenges in 2016, The DAO pioneered governance mechanisms applicable in modern DAOs.
- Maker DAO: Successfully implemented governance rules and quorum requirements, resulting in a sustainable ecosystem.
Future Prospects for BTCMajor and HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO
The future of BTCMajor and the HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO looks promising as blockchain technology evolves. With the growing adoption of cryptocurrencies and increasing user awareness in Vietnam, the platform is positioned for significant impact in the financial sector.
According to a recent survey by Statista, the percentage of Vietnamese internet users interested in cryptocurrencies has risen to 45%. This interest creates a fertile ground for DAOs, particularly those like HIBT, as users seek secure and transparent investment avenues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BTCMajor’s management of the HIBT Vietnam Bond DAO offers an innovative governance model that showcases the power of decentralized decision-making. As Vietnam moves toward becoming a blockchain hub, the importance of strategic governance and effective quorum rules cannot be overstated. By understanding and implementing these principles, BTCMajor can continue to thrive in the rapidly changing landscape of digital assets.
For more details and updates, feel free to explore BTCMajor or check out resources on HIBT.